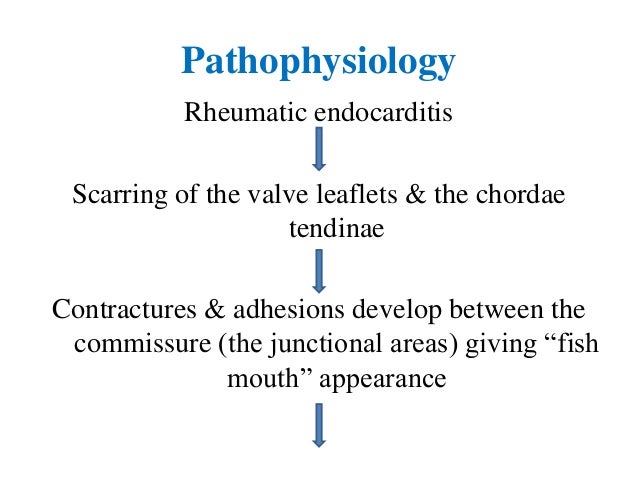
Rheumatic Heart Disease Pathophysiology
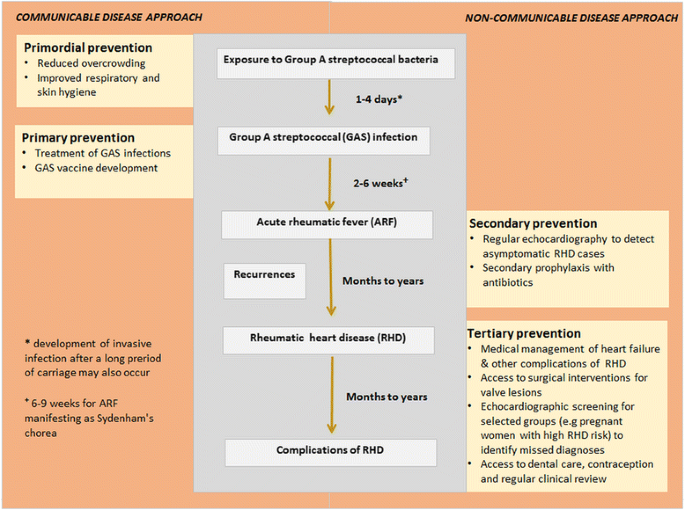
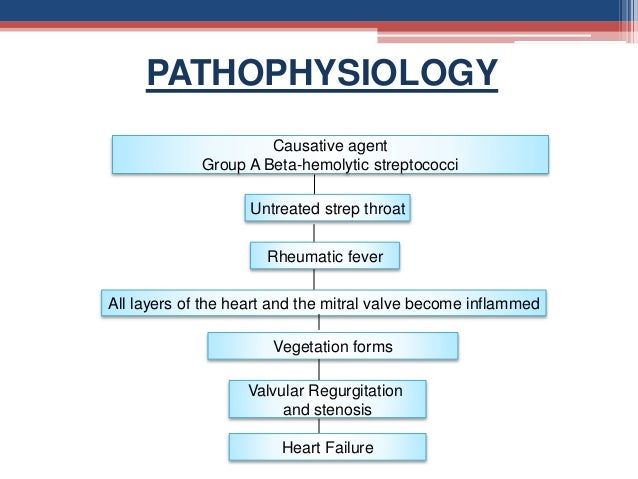
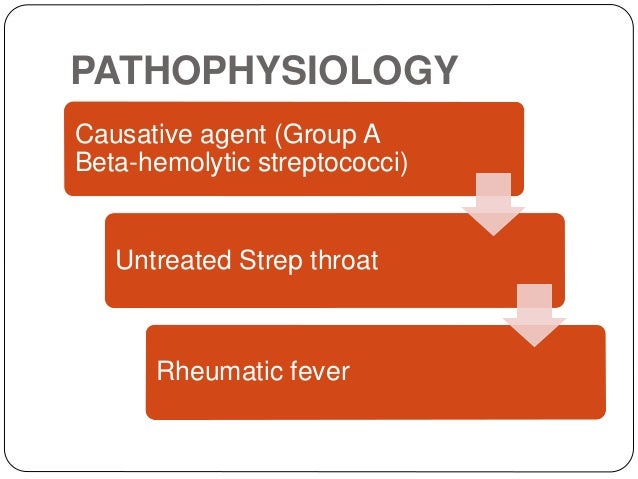
Rheumatic heart disease pathophysiology. Rheumatic fever only occurs as a result of an untreated group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus pharyngeal infection. Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease- due to the etiological factor. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection.
Signs and symptoms include fever multiple painful joints involuntary muscle movements and occasionally a characteristic non-itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. The antigen of beta-hemolytic streptococci reacts. Pathophysiology Diagnosis Complications Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease.
Rheumatic Heart Disease Pathophysiology PDF. The first symptoms of rheumatic heart disease begin with symptoms of. Rheumatic heart disease occurs due to an autoimmune response to rheumatic.
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Fever. Diagnosis of Rheumatic Heart Disease. The pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease rhd is not well understood.
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that develops after being infected by the group A beta-hemolytic Streptococci bacteria. Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart joints skin and brain. A complete case-based review of the essentials of pathophysiology covering all major organs and systems.
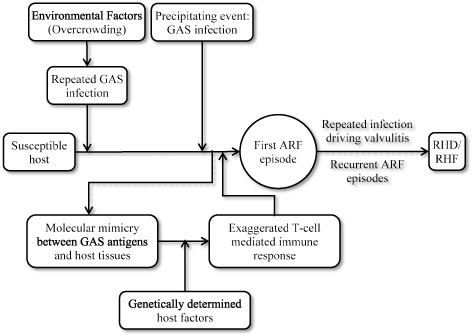
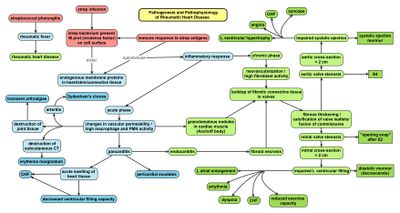
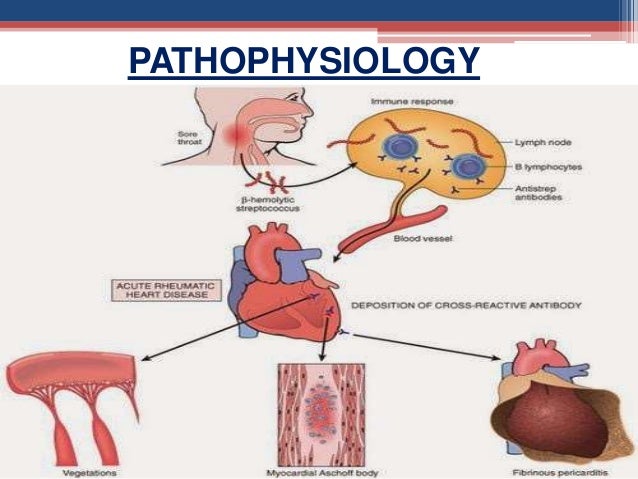
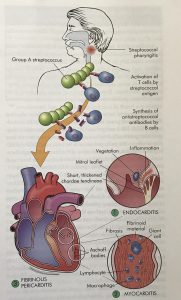
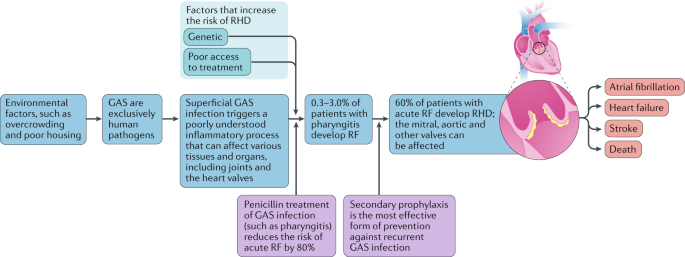
Rheumatic Heart Valve Disease Pathophysiology and Underlying Mechanisms. 2 remodeling of cardiac myocytes. INTRODUCTION Rheumatic fever is a diffuse inflammatory disease characterized by a delayed response to an infection by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci GAS in the tonsilopharyngeal area affecting the heart joints central nervous system skin and subcutaneous tissues.
Much of our understanding of the natural history of the disease stems from seminal studies conducted over 50 years ago13 While disease pathophysiology may. Pathology and pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease.
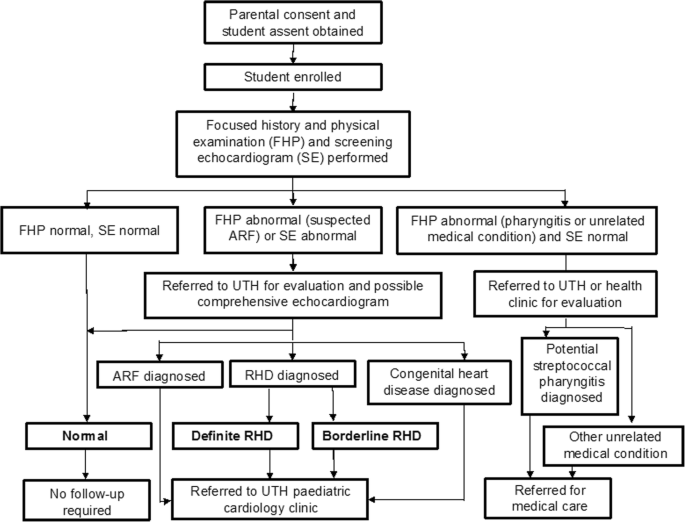
Pediatric prognosis rheumatic heart disease R heumatic heart disease RHD remains a disease of international importance yet little has been published about disease progression in a contemporary cohort.
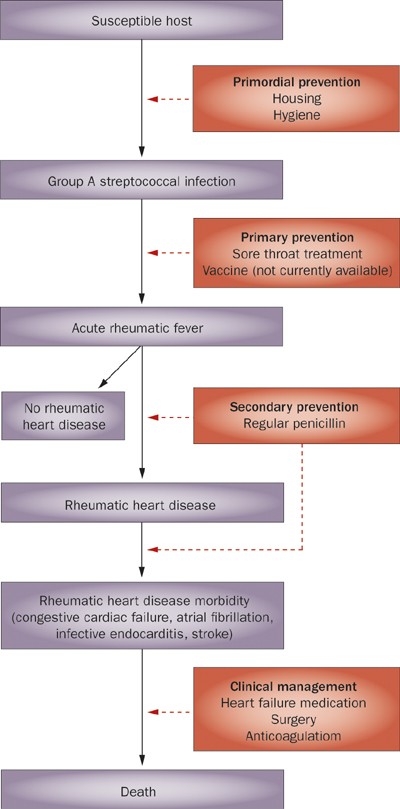
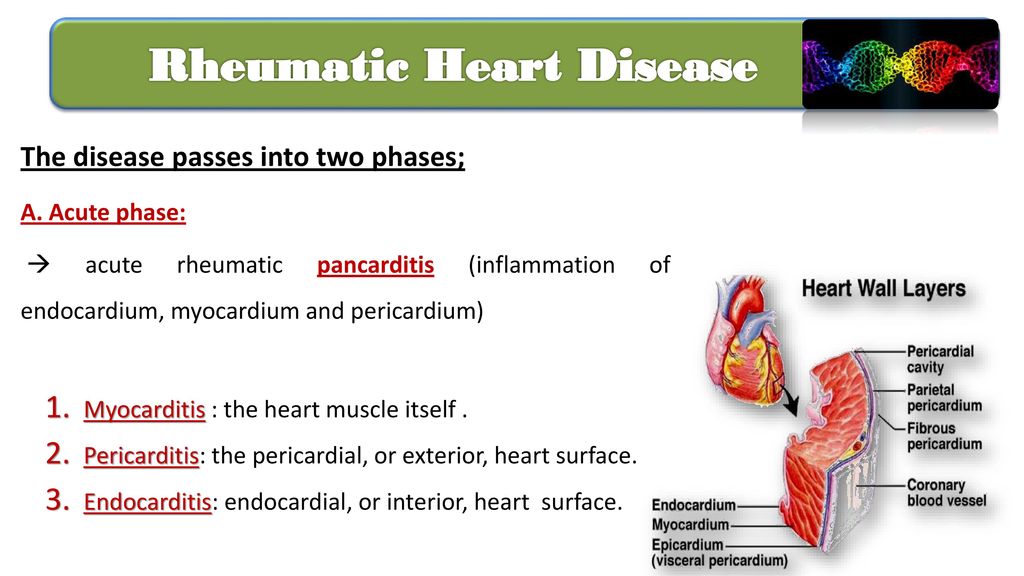
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseRheumatic Heart Fever. It is thought that 40-60 of patients with ARF will go on to developing RHD. However it is known that there are at least three major pathways involved in its development. Rheumatic Heart Disease is the permanent heart valve damage resulting from one or more attacks of ARF. Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart joints skin and brain. RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE Rheumatic heart disease is an immunologic disease characterized by valvular damage or dysfunction followed by one or more episodes of rheumatic fever caused by pharyngeal infection with GAB hemolytic streptococci. Rheumatic heart valve disease RHVD is a post-infectious sequel of acute rheumatic fever resulting from an abnormal immune response to a streptococcal pharyngitis that triggers valvular damage. The heart is involved in about half of the cases. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection.
Rheumatic heart disease occurs due to an autoimmune response to rheumatic. Signs and symptoms include fever multiple painful joints involuntary muscle movements and occasionally a characteristic non-itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. Pathophysiology Diagnosis Complications Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease. INTRODUCTION Rheumatic fever is a diffuse inflammatory disease characterized by a delayed response to an infection by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci GAS in the tonsilopharyngeal area affecting the heart joints central nervous system skin and subcutaneous tissues. Pathology and pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease. Persistent infection of through streptococci. A complete case-based review of the essentials of pathophysiology covering all major organs and systems.





























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rheumatic-heart-disease-1746054_Final-ea5363d837e04f2db79f92f0039206f4.jpg)

Post a Comment for "Rheumatic Heart Disease Pathophysiology"